
英语原文共 57 页,剩余内容已隐藏,支付完成后下载完整资料
Jardine, R. J. (2020). Geacute;otechnique 70, No. 1, 3–59 [https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.18.RL.001]
岩土工程,能源与气候变化:第56届兰金演讲
RICHARD J. JARDINE*
岩土工程已经足够成熟,有助于解决社会的一些巨大挑战。第56届兰金讲座认为,最紧迫的全球问题之一是保持重要的能源供应,同时认识、减轻和减少化石燃料消耗对气候的影响。这份书面版本报告了与这些宽泛的问题相关的岩土工程研究 ,同时考虑了三个主要部分中的配对主题 ,并特别用具体的实际示例来说明这些主题。第一部分侧重于介绍近海碳氢化合物生产,考虑在了解和设计支持大多数大陆架平台的打入桩方面的进展,然后话题转移到可能影响更深层水开发的大型水下滑坡。第二部分介绍了对永久冻土地区气候变化的岩土工程影响的研究,以及有助于减少因气候变化加剧的洪水风险的泥炭地研究。 第三部分介绍了用于提高多桩和单堆支持涡轮机的可再生海上风能经济性的研究。将地质学和严谨分析及先进的实验室和现场实验相结合,对于解决所考虑的复杂岩土工程问题至关重要,仔细进行全面检查和监测也至关重要。与工业界和学术界的同事密切合作是所述研究的核心,并强调了许多合作者的贡献。结论部分确定了六个专题领域中还需要充分解决的一些关键问题的例子。
关键词: 基脚/地基;滑坡;桩和打桩
GEOTECHNICS AND ENERGY
Geotechnics has developed over the last century into a discipline that engages thousands of professional specialists worldwide. The first two conferences of the International Society for Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, held in 1936 and 1948, mark perhaps the two most significant events in the practical assimilation of the seminal contri- butions of Coulomb (1776), Rankine (1857), Prandtl (1920), Terzaghi (1925), Hvorslev (1937) and other early pioneers. Tremendous advances have followed since, many of which have been recorded in the 55 Rankine Lectures delivered before this contribution, ranging from critical laboratory experiments to rigorous theoretical investigations and from computer coding triumphs through to large-scale field studies. Research motives have ranged from pure curiosity through to a wish to address urgent industrial or societal questions; these researchersrsquo; combined efforts have created extensive bodies of new knowledge.
As geotechnics matures, ever greater resources appear necessary to achieve significant advances. Research teams are often encouraged to focus their efforts on the lsquo;grand challengesrsquo; that are most critical to human societies and quality of life, as well as sustaining or improving the quality of our natural and built environments. Among the most pressing questions to resolve over the next decades are those related to energy production. Choosing this main theme reflects the seminal contributions in thermodynamics of
Manuscript received 19 April 2018; manuscript accepted 6 June
2019. Published online ahead of print 16 July 2019.
Discussion on this paper closes on 1 June 2020, for further details see p. ii.
Published with permission by the ICE under the CC-BY 4.0 license. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
* Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Imperial
College London, London, UK.
Rankine (1850) that led, with his later publications, to lasting international recognition. For example, the process employed in steam-operated electricity generators is known widely as the lsquo;Rankine cyclersquo;.
Pasten amp; Santamarina (2012) present convincing evidence of the social benefits of increasing energy provision per capita, especially in the developing world. Collating data from the worldrsquo;s 22 most populous nations, they show that positive outcomes, including greater average life expectancy, longer schooling years and higher incomes correlate directly with the 5 to 10 kW/capita consumption range enjoyed by economically leading nations. Negative measures such as infant mortality rates fall greatly as energy consumption levels rise. Conservation measures and other factors are leading to energy use per capita reducing in some advanced nations (see e.g. World Bank, 2018). However, global demand is currently growing by 20% per decade as the worldrsquo;s less prosperous populations gradually achieve better living standards.
More than 85% of global energy production is derived currently from fossil fuels that produce large masses of carbon dioxide (CO2) by-product according to Natural Resources Canada (NRCan, 2017). Maintaining or increas- ing production cannot be reconciled with the internationally acknowledged environmental need to cut greenhouse gas emissions drastically in the decades ahead. Each kWh of electricity generated from coal produces approximately 1 kg of carbon dioxide, depending on coal grade, while oil and natural gas fuel produce less, around 0·75 and 0·5 kg/kWh, respectively. Meeting the internationally agreed greenhouse gas targets calls for a rebalancing of energy production away from coal and towards gas and renewable sources. There remains intense international debate on how to achieve such changes without disrupting energy supplies, blocking economic growth or holding back developing nations.
Engineers from all disciplines are contributing to the worldrsquo;s lsquo;grand challengersquo;. Geotechnical researchers are active in areas ranging from ground energy storage and production schemes
3
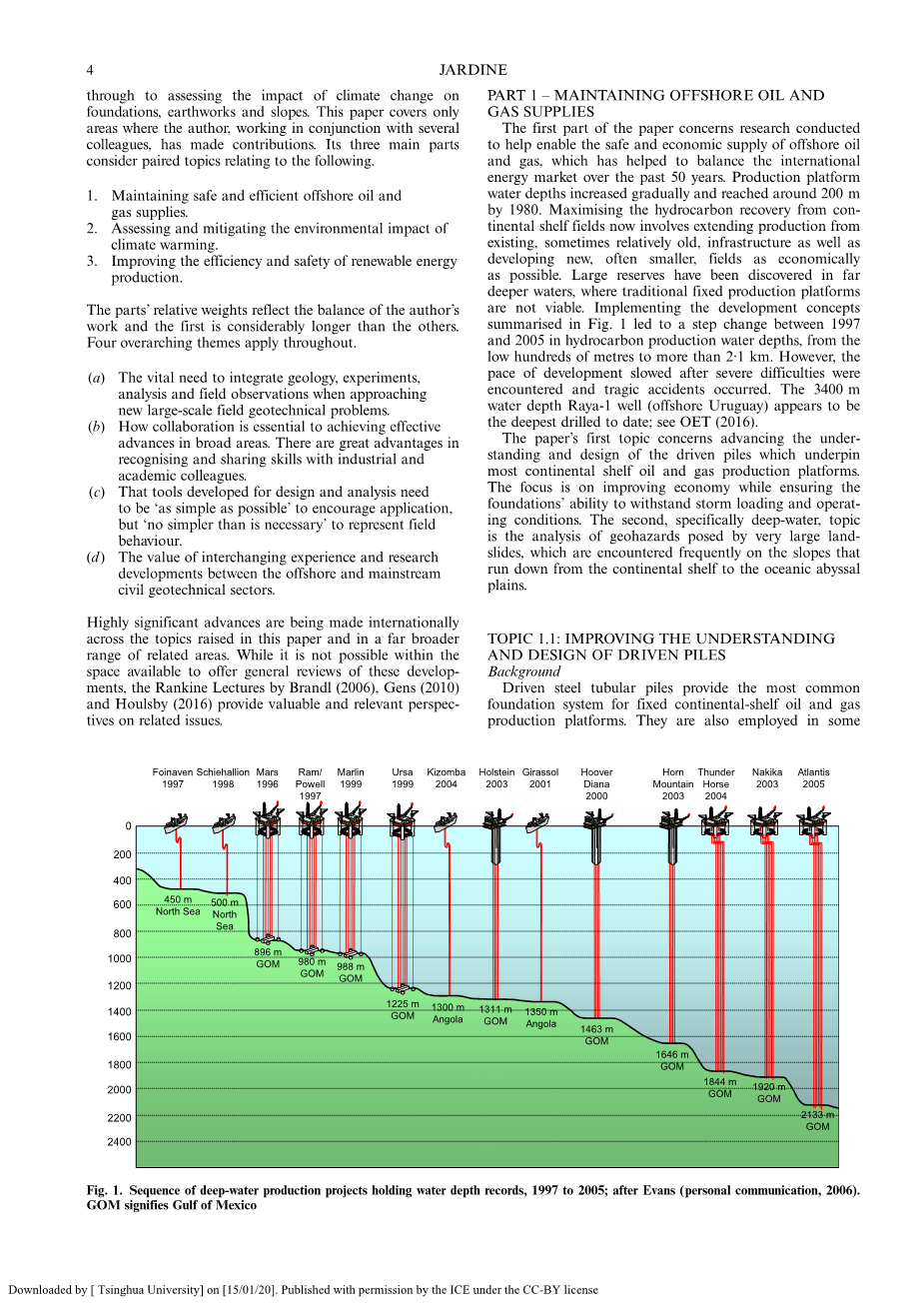
4 JARDINE
through to assessing the impact of climate change on foundations, earthworks and slopes. This paper covers only areas where the author, working in conjunction with several colleagues, has made contributions. Its three main parts consider paired topics relating to the following.
- Maintaining safe and efficient offshore oil and gas supplies.
- Assessing and mitigating the environmental impact of climate warming.
- Improving the efficiency and safety of renewable energy production.
The partsrsquo; relative weights reflect the balance of the authorrsquo;s work and the first is considerably longer than the others. Four overarching themes apply throughout.
-
The vital need to integrate geology, experiments,
剩余内容已隐藏,支付完成后下载完整资料
资料编号:[263865],资料为PDF文档或Word文档,PDF文档可免费转换为Word
以上是毕业论文外文翻译,课题毕业论文、任务书、文献综述、开题报告、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。


